

DWG's mission is to materially contribute to the effective formulation of national and regional energy policies that will support economic growth, energy security and environmental protection.
DWG provides policy analysis, model development, training and capacity building in the field of integrated energy system planning.
Expertise and Experience
NDC
ANALYSIS
POLICY
ANALYSIS
US MODEL
DEVELOPMENT
INTERNATIONAL
WORK
MARKAL - TIMES MODEL
& COLLABORATION
NDC Pathway Analyses
VIETNAM: GETTING ON A LOW-CARBON ENERGY PATH TO ACHIEVE NDC TARGET, World Bank (2018 to 2020)
The World Bank and the Partnership for Market Readiness (PMR) in Vietnam, selected DWG to develop the analytical tools and capabilities to assist the government in determining viable pathways to achieve the emission reduction commitments made in its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC). The project supported the Ministry of Industry and Trade (MOIT) to prepare a roadmap of mitigation measures for the energy sector contribution to the Government of Vietnam’s upcoming 2020 NDC commitments. The analysis identified the most cost-effective policies and measures for the supply and power sectors, 12 industry subsectors, and the residential and commercial sectors. The analysis was performed using the TIMES-Starter model, which was tailored to the Vietnam energy system to produce the multi-region TIMES-Vietnam model. The analysis has recommended a roadmap of priority actions (pathways) and set of specific metrics for each sector, including investment needs, GHG emission reductions and mitigation cost effectiveness, which the MOIT can use to craft their unconditional and conditional NDC targets. The figures show the percent contribution of various power sector measures to achieve a 25% reduction target, along with a measure of the effectiveness of individual measures that weighs the costs vs reduction to determine the attractiveness of each option in meeting the target. Presentations based upon TIMES-Vietnam mitigation analysis were made at COP24 and COP25 by MOIT. The project also included training and mentoring to ensure that a local team of experts is able to take over ongoing stewardship and application of the TIMES-Vietnam model.
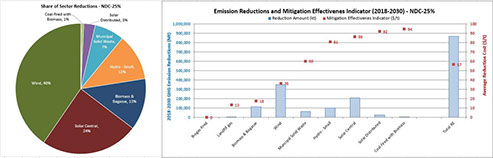
WB-PMR_Vietnam_NDC Final Report_03282020-Clean.pdf
Costa Rica: Assessing Climate Mitigation Pathways To Support NDC Implementation
 The World Bank and the Partnership for Market Readiness (PMR) in Costa Rica, selected DWG to develop the analytical tools and capabilities to assist the government in determining viable pathways to achieve the emission reduction commitments made in its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC). A secondary goal was to establish the in-country capacity that will allow continuous improvements and ongoing application of the methodology to examine new issues, options, technologies and policies as circumstances dictate to inform future NDC and policy developments. Furthermore, the resulting platform was designed to be readily applicable, transferable and reproducible by PMRs in other countries. The DWG team worked with local experts and key stakeholders to:
The World Bank and the Partnership for Market Readiness (PMR) in Costa Rica, selected DWG to develop the analytical tools and capabilities to assist the government in determining viable pathways to achieve the emission reduction commitments made in its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC). A secondary goal was to establish the in-country capacity that will allow continuous improvements and ongoing application of the methodology to examine new issues, options, technologies and policies as circumstances dictate to inform future NDC and policy developments. Furthermore, the resulting platform was designed to be readily applicable, transferable and reproducible by PMRs in other countries. The DWG team worked with local experts and key stakeholders to:
Identify policies and measures politically, technically, and economically viable for Costa Rica;
Develop a country-specific energy systems model with validated input parameters and resulting Baseline scenario;
Develop a Planned policy scenario to assess existing and proposed mitigation policies and actions;
Develop Enhanced policy scenarios necessary for Costa Rica to achieve its NDC targets, and Build local capacity to take over stewardship and ongoing use of the national energy planning platform.
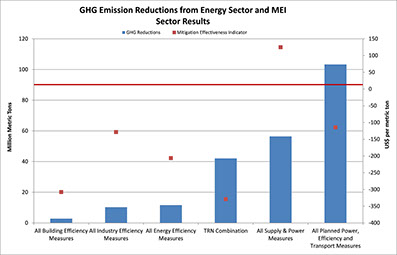
Costa Rica set a very ambitious GHG mitigation target in its NDC. Achieving these goals will require aggressive decarbonization actions and policies, particularly in the transport, non-electrical energy, agriculture, and waste sectors. This project developed improved analytical tools and capabilities such as the mitigation effectiveness indicator shown
here. The resulting country-specific modeling framework was established with the objective of assisting the government of Costa Rica in assessing alternative pathways to achieve the emission reduction commitments made in its NDC. The model was used to analyze of the contributions, costs and impacts of about 75 sector-specific policies and measures, and combinations thereof, to enable the country to achieve its ambitious NDC targets. Initial focus was on the power and transportation sectors, but included buildings and industry sectors. Future added capabilities are planned to add non-energy GHG sectors to the optimization framework.
Costa Rica: Assessing Climate Mitigation Pathways To Support NDC Implementation
Clean Energy Georgia - Strategic Planning Component
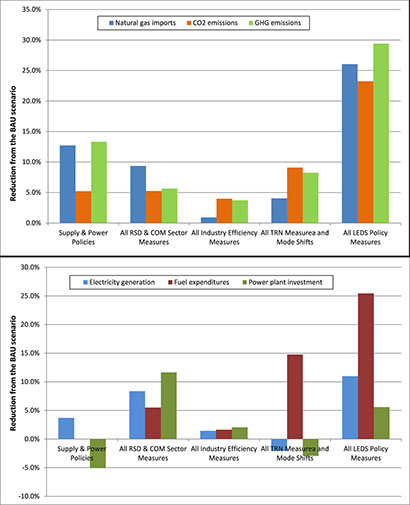 The project supported increased climate change mitigation by building capacity in climate change mitigation measures; increasing private sector investment in energy efficiency and green buildings; raising public awareness; and strengthening Government of Georgia capacity to develop and implement a national Low Emissions Development Strategy (LEDS) program. DWG supported the National LEDS Steering Committee and associated technical working groups, including providing advisory assistance to articulate concrete actions, policies, programs and implementation plans under the US-Georgia bilateral Enhanced Capacity for LEDS initiative. DWG activities supported the updating and improvements to the MARKAL-Georgia national energy sector planning model to cover all GHG emissions from the energy sector and to expand the model to also cover the non-energy sector emissions and mitigation measures. DWG has worked with local experts and the Analytical Department of the Ministry of Energy and the Ministry of Environment’s Climate Change Office to develop LEDS measures in conjunction with expert working groups. In 2015, DWG used the model to evaluate possible Intended Nationally Determined Contribution (INDC) targets for Georgia, and in 2016 performed a detailed examination of specific sectoral mitigation measure to provide analytical underpinnings to facilitate determination of policies for achieving the NDC targets. Finally, in 2017 DWG used the MARKAL-Georgia model and the best available data to combine non-energy sector baseline emissions and mitigation measures with the energy sector analysis to generate a cost-effective implementation strategy for meeting Georgia’s full NDC target.
The project supported increased climate change mitigation by building capacity in climate change mitigation measures; increasing private sector investment in energy efficiency and green buildings; raising public awareness; and strengthening Government of Georgia capacity to develop and implement a national Low Emissions Development Strategy (LEDS) program. DWG supported the National LEDS Steering Committee and associated technical working groups, including providing advisory assistance to articulate concrete actions, policies, programs and implementation plans under the US-Georgia bilateral Enhanced Capacity for LEDS initiative. DWG activities supported the updating and improvements to the MARKAL-Georgia national energy sector planning model to cover all GHG emissions from the energy sector and to expand the model to also cover the non-energy sector emissions and mitigation measures. DWG has worked with local experts and the Analytical Department of the Ministry of Energy and the Ministry of Environment’s Climate Change Office to develop LEDS measures in conjunction with expert working groups. In 2015, DWG used the model to evaluate possible Intended Nationally Determined Contribution (INDC) targets for Georgia, and in 2016 performed a detailed examination of specific sectoral mitigation measure to provide analytical underpinnings to facilitate determination of policies for achieving the NDC targets. Finally, in 2017 DWG used the MARKAL-Georgia model and the best available data to combine non-energy sector baseline emissions and mitigation measures with the energy sector analysis to generate a cost-effective implementation strategy for meeting Georgia’s full NDC target.
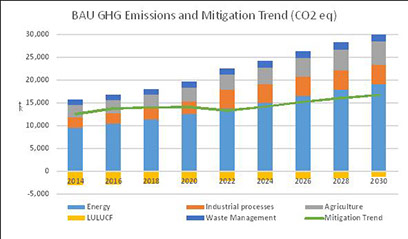
Ukraine Municipal Energy Reform Project (MERP) - Strategic Planning Component
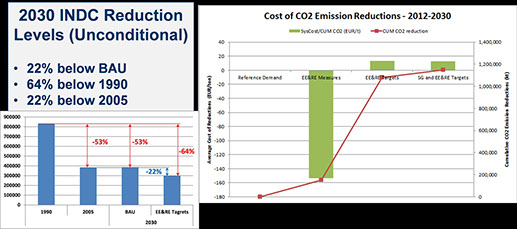 This USAID funded project was designed to enhance Ukraine’s energy security through increased end-use energy efficiency combined with increased production of clean energy in large towns and cities. DWG was responsible for supporting the advancement of the TIMES-Ukraine model to more broadly address low-emission development strategies (LEDS), and to build capacity in the relevant ministries and other key stakeholders in Ukraine. DWG experts have supported the updating and improvements to the TIMES-Ukraine national energy sector planning model to cover all GHG emissions from the energy sector and to expand the model to also cover the non-energy sector emissions and mitigation measures. DWG worked closely with the local expert team, at the National Academy of Sciences Institute for Economic Forecasting, to develop LEDS measures and evaluate possible Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDC) targets for Ukraine. In addition, DWG implemented and showcased an on-line portal for disseminating model results using an intuitive scenario generator approach.
This USAID funded project was designed to enhance Ukraine’s energy security through increased end-use energy efficiency combined with increased production of clean energy in large towns and cities. DWG was responsible for supporting the advancement of the TIMES-Ukraine model to more broadly address low-emission development strategies (LEDS), and to build capacity in the relevant ministries and other key stakeholders in Ukraine. DWG experts have supported the updating and improvements to the TIMES-Ukraine national energy sector planning model to cover all GHG emissions from the energy sector and to expand the model to also cover the non-energy sector emissions and mitigation measures. DWG worked closely with the local expert team, at the National Academy of Sciences Institute for Economic Forecasting, to develop LEDS measures and evaluate possible Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDC) targets for Ukraine. In addition, DWG implemented and showcased an on-line portal for disseminating model results using an intuitive scenario generator approach.
Ukraine INDC Analysis_SummaryBrief.pdf
Center for Climate Strategies: Strategic Investment Project
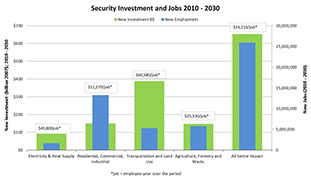 DWG provided the analytic foundation to support a CCS study on the “Impacts of Comprehensive Climate and Energy Policy Options on the U.S. Economy.” The study used the DWG US National MARKAL model to analyze national-level costs and benefits of implementing clean energy policies that are popular at the state level. The study identified policy actions designed to simultaneously achieve overlapping, net positive economic, security, and environmental benefits. The study also identified the investment requirements for each and the likely sources of public and private financing that would benefit from these specific public sector actions.
DWG provided the analytic foundation to support a CCS study on the “Impacts of Comprehensive Climate and Energy Policy Options on the U.S. Economy.” The study used the DWG US National MARKAL model to analyze national-level costs and benefits of implementing clean energy policies that are popular at the state level. The study identified policy actions designed to simultaneously achieve overlapping, net positive economic, security, and environmental benefits. The study also identified the investment requirements for each and the likely sources of public and private financing that would benefit from these specific public sector actions.
Executive Summary Report
Department of Energy (DOE): Integrated Benefits Analysis of Advanced Technology Programs
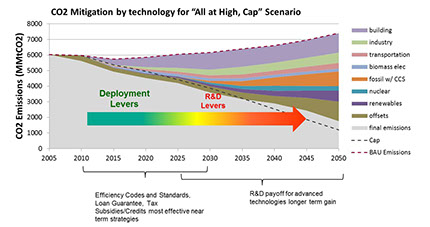 DWG assisted the DOE Office of Program Analysis and Evaluation to perform an integrated analysis of the costs and benefits of the various DOE advanced energy programs as part of the Budget development process. DWG developed a tailored version of its US national MARKAL model for this work. The analyses, involving hundreds of model runs, explored the impacts of increasing or decreasing funding to various programs to help identify a more optimal mix of agency resources. DWG also performed specific model analyses based on policy questions of importance to DOE. This work was performed as part of advising the FY2012, FY2013 and FY2014 budgets.
DWG assisted the DOE Office of Program Analysis and Evaluation to perform an integrated analysis of the costs and benefits of the various DOE advanced energy programs as part of the Budget development process. DWG developed a tailored version of its US national MARKAL model for this work. The analyses, involving hundreds of model runs, explored the impacts of increasing or decreasing funding to various programs to help identify a more optimal mix of agency resources. DWG also performed specific model analyses based on policy questions of importance to DOE. This work was performed as part of advising the FY2012, FY2013 and FY2014 budgets.
Natural Resources Defense Council (NRDC): Analysis of US CO2 Reduction Legislation
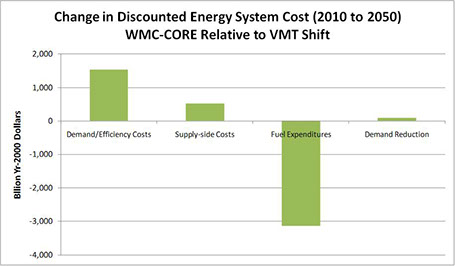 Over a 3-year period, the DWG team worked with NRDC to conduct analyses of proposed CO2 Cap and Trade legislation under consideration in the US Congress. Analyses focused on various legislative initiatives, including the Waxman-Markey bill, the Lieberman-Warner bill, and the Sanders-Boxer bill. The analyses were performed using an improved and updated version of the US national MARKAL model originally developed by the Environmental Protection Agency’s Office of Research and Development with support from the DWG principals. The analysis shows that the proposed CO2 reduction targets are achievable with minimal increase in the overall cost of the energy system.
Over a 3-year period, the DWG team worked with NRDC to conduct analyses of proposed CO2 Cap and Trade legislation under consideration in the US Congress. Analyses focused on various legislative initiatives, including the Waxman-Markey bill, the Lieberman-Warner bill, and the Sanders-Boxer bill. The analyses were performed using an improved and updated version of the US national MARKAL model originally developed by the Environmental Protection Agency’s Office of Research and Development with support from the DWG principals. The analysis shows that the proposed CO2 reduction targets are achievable with minimal increase in the overall cost of the energy system.
NRDC Report
US National, Region and State-level Model Development
US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Office of Research and Development (ORD), Nine Region US Model (US9r)
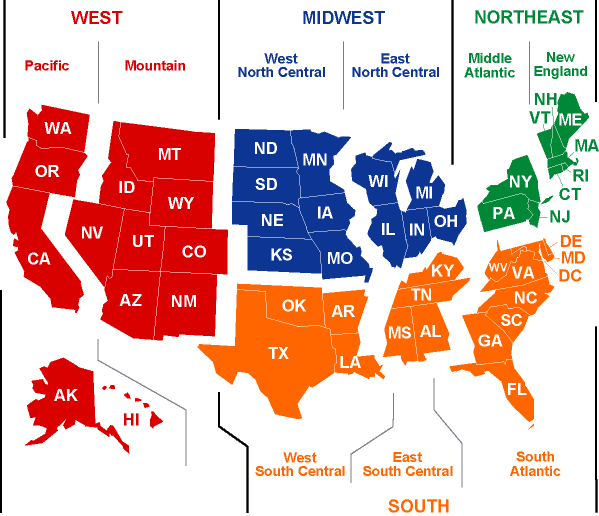 The DWG team, supported by OnLocation, Inc., developed the key components the 1st multi-region USMARKALS model, US9r, which models the US energy system according to the nine census divisions. US9r is used by EPA-ORD to look at climate change and longer term clean air issues out to 2050. EPA-ORD has made US9r available to interested parties through the Environmental Science Connector website.
The DWG team, supported by OnLocation, Inc., developed the key components the 1st multi-region USMARKALS model, US9r, which models the US energy system according to the nine census divisions. US9r is used by EPA-ORD to look at climate change and longer term clean air issues out to 2050. EPA-ORD has made US9r available to interested parties through the Environmental Science Connector website.
Northeast States for Coordinated Air Use Management: NE-12 Model Development
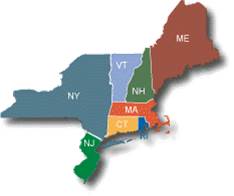 The DWG team, supported by OnLocation, Inc. designed and implemented the first multi-state MARKAL/TIMES model of the US. Initially a 6-state New England MARKAL model was prepared as part of the New England Governors/Eastern Canadian Premier climate initiative. Later the model was expanded to a 12-state model of the Northeast covering the states from Maine to Washington, DC. The framework has been used to examine issues for numerous states in the Northeast including New York, Maryland, Massachusetts, and Connecticut. More information on NE-12 can be found at http://www.nescaum.org/topics/ne-markal-model.
The DWG team, supported by OnLocation, Inc. designed and implemented the first multi-state MARKAL/TIMES model of the US. Initially a 6-state New England MARKAL model was prepared as part of the New England Governors/Eastern Canadian Premier climate initiative. Later the model was expanded to a 12-state model of the Northeast covering the states from Maine to Washington, DC. The framework has been used to examine issues for numerous states in the Northeast including New York, Maryland, Massachusetts, and Connecticut. More information on NE-12 can be found at http://www.nescaum.org/topics/ne-markal-model.
US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Office of Research and Development (ORD):
National MARKAL Model Development
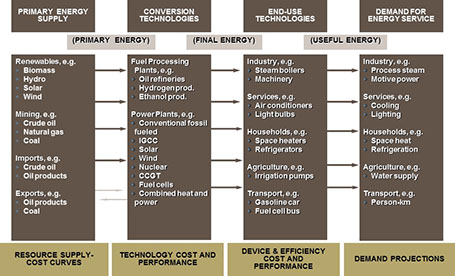 DWG experts provided basic and advanced training to EPA-ORD and supported the development, improvement and expansion of a national MARKAL model. DWG supported the Atmospheric Protection Branch to develop and assess the environmental and economic consequences of energy technology futures scenarios for the U.S. as part of a study on the air quality impacts of climate change DWG also developed a methane emissions module for the national MARKAL model which was used by the EPA Methane to markets program.
DWG experts provided basic and advanced training to EPA-ORD and supported the development, improvement and expansion of a national MARKAL model. DWG supported the Atmospheric Protection Branch to develop and assess the environmental and economic consequences of energy technology futures scenarios for the U.S. as part of a study on the air quality impacts of climate change DWG also developed a methane emissions module for the national MARKAL model which was used by the EPA Methane to markets program.
Integrated Energy Models for Transition & Developing Countries
Armenia: Market Liberalization & Electricity Trade (MLET) Program; Least-cost Energy Development Plan (LCEDP), USAID (2018-2019)
DWG experts guided and supported researchers from the Scientific Research Institute of Energy (SRIE) in the tailoring of the TIMES-Starter model into the TIMES-Armenia national energy sector planning model on behalf of the Ministry of Energy Infrastructures and Natural Resources (MEINR). DWG has also reviewed and supported SRIE in the development of a Baseline scenario and in the design of specific energy sector development scenarios that underpinned the LCEDP. The analysis highlighted the potential role that renewable electric generation, in particular central solar PV, can play to both meet growing electricity demand and contribute to emission reductions in Armenia. The draft LCEDP: 2020-2036 was reviewed in detail by DWG prior to its publication in November 2019.
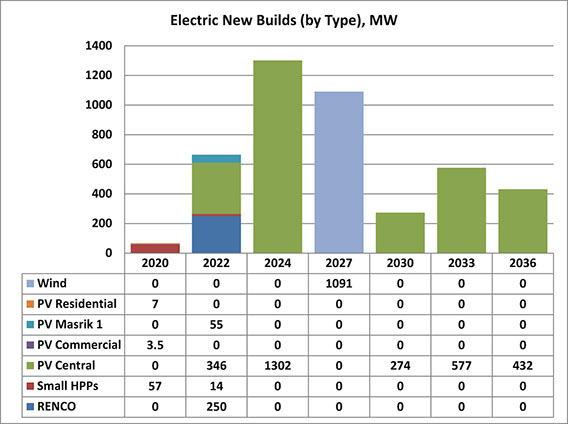
LCEDP Report_with Append_Eng_Nov 7.pdf
World Bank, Thirsty Energy Initiative: Case studies in South Africa and China
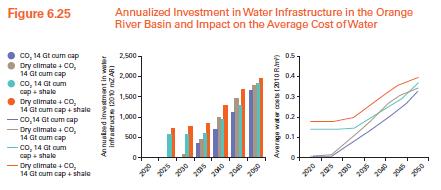 The World Bank (WB) has embarked on a global initiative called Thirsty Energy to assist countries to tackle water and energy management challenges in an integrated manner, rather than through the traditional decoupled approach. DWG has supported the Bank in the development of this initiative from the concept paper stage, and has coordinated the first two Thirsty Energy case studies in South Africa and China. The methodology focuses on integrating the various water supply options in a least-cost energy system optimization model. The resulting “water-smart’ energy model ensures that the cost of water is fully captured as energy sector investments are planned. The finding of these two case studies have demonstrated the process and type of techniques that can be employed to examine the water-energy nexus and the insights that can be gained from integrated energy-water planning. A number of relevant energy-water policy scenarios in South Africa were explored, and the results show that specific energy sector policies can have significant implication for both new investment in water supply infrastructure and in some cases can lead to stranded water supply investments, and vice versa, reinforcing the importance of planning the water-energy nexus in an integrated manner.
The World Bank (WB) has embarked on a global initiative called Thirsty Energy to assist countries to tackle water and energy management challenges in an integrated manner, rather than through the traditional decoupled approach. DWG has supported the Bank in the development of this initiative from the concept paper stage, and has coordinated the first two Thirsty Energy case studies in South Africa and China. The methodology focuses on integrating the various water supply options in a least-cost energy system optimization model. The resulting “water-smart’ energy model ensures that the cost of water is fully captured as energy sector investments are planned. The finding of these two case studies have demonstrated the process and type of techniques that can be employed to examine the water-energy nexus and the insights that can be gained from integrated energy-water planning. A number of relevant energy-water policy scenarios in South Africa were explored, and the results show that specific energy sector policies can have significant implication for both new investment in water supply infrastructure and in some cases can lead to stranded water supply investments, and vice versa, reinforcing the importance of planning the water-energy nexus in an integrated manner.
The report on the South Africa case study can be found at :
https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/26255
The report on the China case study can be found at:
https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/29509
The Thirsty Energy Case Studies were summarized in new book, “Limiting Global Warming to Well Below 2 °C: Energy System Modelling and Policy Developments,” which is available online at https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-319-74424-7.
USAID: Regional Energy Security and Market Development (RESMD) - Strategic Planning
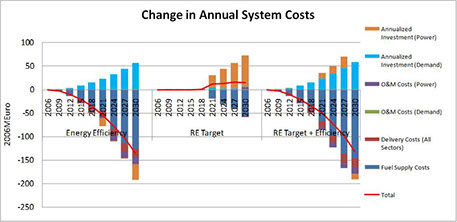 Between 2005 and 2012, the DWG team supported two major USAID projects for the Energy Community Treaty countries of Southeast Europe and Eurasia to develop a consistent regional approach for assessing energy demand, investment requirements and cooperation opportunities by building national energy system planning models and capability. As part of the first project, Southeast Europe Regional Energy Demand Planning Project (SEE-REDP), which was conducted from 2005 to 2007, the DWG team created energy system planning capability by organizing and training teams from eight South East European countries, and worked closely with them to develop MARKAL-based national energy planning models for each country. The data for each model was assembled by the country experts, who were trained by the DWG team to understand and use their models to analyze a range of planning scenarios and priority issues facing the countries. Specific analyses focused on future energy requirements and the implications of economic growth in the region within the framework of the Energy Community.
Between 2005 and 2012, the DWG team supported two major USAID projects for the Energy Community Treaty countries of Southeast Europe and Eurasia to develop a consistent regional approach for assessing energy demand, investment requirements and cooperation opportunities by building national energy system planning models and capability. As part of the first project, Southeast Europe Regional Energy Demand Planning Project (SEE-REDP), which was conducted from 2005 to 2007, the DWG team created energy system planning capability by organizing and training teams from eight South East European countries, and worked closely with them to develop MARKAL-based national energy planning models for each country. The data for each model was assembled by the country experts, who were trained by the DWG team to understand and use their models to analyze a range of planning scenarios and priority issues facing the countries. Specific analyses focused on future energy requirements and the implications of economic growth in the region within the framework of the Energy Community.
Asian Development Bank: Pakistan Integrated Energy Model
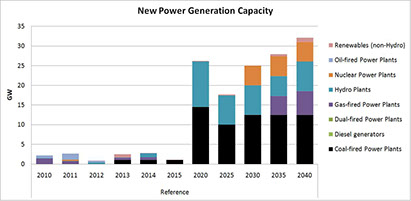 The DWG team developed a TIMES energy system planning model that integrates Pakistan’s energy demand and supply situation for all sectors of the country. The DWG team worked with local experts and the Planning Commission of the Government of Pakistan to develop needed data, including resource cost-supply curves and useful energy demand projections for Pakistan. Training and capacity building was provided for a local energy planning team, comprised of seven institutions, that enabled them to analyze possible energy futures, assess the impacts of various policy scenarios and support more informed decision-making.
The DWG team developed a TIMES energy system planning model that integrates Pakistan’s energy demand and supply situation for all sectors of the country. The DWG team worked with local experts and the Planning Commission of the Government of Pakistan to develop needed data, including resource cost-supply curves and useful energy demand projections for Pakistan. Training and capacity building was provided for a local energy planning team, comprised of seven institutions, that enabled them to analyze possible energy futures, assess the impacts of various policy scenarios and support more informed decision-making.
PAK-IEM Final Workshop Presentation PDF
World Bank: Integrating Energy/Water/Economy Modeling
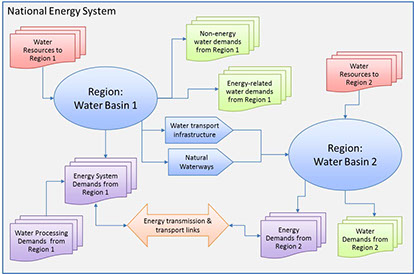 The need to understand the interactions between energy and water use is growing relative to the planning and development challenges surrounding sustainable access to water, land, food, energy and a clean environment – especially as the stresses created by population, economic development and climate change impacts increase. The World Bank engaged DWG to assess the current state of knowledge and methods for addressing the energy-water nexus, as well as the economic impacts, and to provide World Bank project leaders with a better understanding of the available methodologies and approaches that can provide quantitative information on energy-water trade-offs.
The need to understand the interactions between energy and water use is growing relative to the planning and development challenges surrounding sustainable access to water, land, food, energy and a clean environment – especially as the stresses created by population, economic development and climate change impacts increase. The World Bank engaged DWG to assess the current state of knowledge and methods for addressing the energy-water nexus, as well as the economic impacts, and to provide World Bank project leaders with a better understanding of the available methodologies and approaches that can provide quantitative information on energy-water trade-offs.
In the second phase of this initiative, DWG is supporting the Bank as it looks for candidate countries to actually undertake the linking of appropriate energy, water and economic models to demonstrate various platforms for examine the nexus. The intention is to use these a case studies that will be transferable to other interested countries. One such case study is under development with the University of Cape Town, Energy Research Centre. The Bank is also in discussions with China and Morocco, both of which are enthusiastic about the Thirsty Energy initiative.
http://www.worldbank.org/thirstyenergy
Kuwait: Economic Analysis of Nuclear and Renewable Energy Options
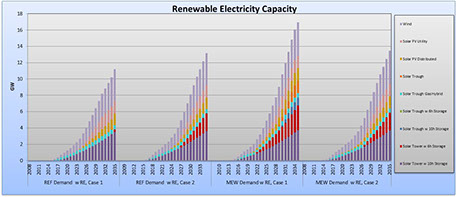 The DWG team performed three studies for Kuwait institutions between 2010 and 2012. The first study, done for the Kuwait National Nuclear Energy Committee (KNNEC), developed a Power and Water Model for the State of Kuwait (KPW), which covered electricity generation and desalinated water production. This initial KPW model was used to analyze the economic value of Kuwait developing a nuclear power program. The study found that nuclear power could provide a significant economic savings, in the range of US$20 billion by 2030 and growing to over US$100 billion by 2050.
The DWG team performed three studies for Kuwait institutions between 2010 and 2012. The first study, done for the Kuwait National Nuclear Energy Committee (KNNEC), developed a Power and Water Model for the State of Kuwait (KPW), which covered electricity generation and desalinated water production. This initial KPW model was used to analyze the economic value of Kuwait developing a nuclear power program. The study found that nuclear power could provide a significant economic savings, in the range of US$20 billion by 2030 and growing to over US$100 billion by 2050.
The second study, performed for the Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research (KISR), further developed the KPW model through the addition of new renewable energy (RE) supply technologies and evaluated four scenarios for the energy supply system to meet the forecasted power and water demand. Two scenarios were based on an energy supply mix consisting of fossil, nuclear, and the most economical RE technologies mix, and two scenarios based on an energy supply mix consisting of fossil and the most economical RE technologies mix. The study found that RE technologies produced their own economic savings and offset some of the projected nuclear capacity.
The third study, also performed for KISR, updated the projections for future crude oil and natural gas prices as well as the projected cost and performance characteristics of the RE technologies of interest to Kuwait, and analyzed the potential for these RE technologies to cost-effectively meet part of Kuwait’s national energy demand. The study showed that several RE technologies have the potential to make significant contributions to electricity and water production and to produce a net-back savings to the economy, estimated at between US$12 and $40 billion between now and 2035. The RE technologies that are projected to have a significant cost-effective impact include Solar Trough Hybrids, Wind Power, Solar Towers with Storage, and Solar PV utility-scale. The study projected the cost-effective share of RE generation that could be in place by 2035 ranges from 24% to 33%.
Economic Analysis of Clean Energy Options for Kuwait PDF
USAID: Enhance Capacity – Low Emissions Development Strategy; Integrated Regional Model for the Energy Community
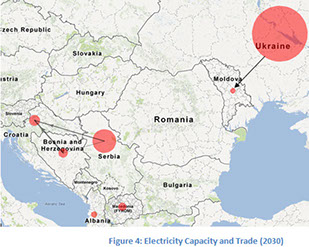 Building on the accomplishments of the RESMD undertaking, that realized MARKAL/TIMES models for seven (7) of the Energy Community (EC), USAID has turned to DWG to link the national model (and create reduced form models for Kosovo and Montenegro) to establish a pan-EC planning frame, EC-TIMES.
Building on the accomplishments of the RESMD undertaking, that realized MARKAL/TIMES models for seven (7) of the Energy Community (EC), USAID has turned to DWG to link the national model (and create reduced form models for Kosovo and Montenegro) to establish a pan-EC planning frame, EC-TIMES.
Stanford Program on Energy and Sustainable Development (PESD): China cities
The DWG team members coordinated the design, development and review of greater metropolitan MARKAL models for Beijing, Guangdong, and Shanghai that were used to examine the implications of increased availability of natural gas in these regions. At the request of PESD, DWG provided training and mentoring of local China experts as they looked to examine the future potential role of natural gas in major metropolitan areas.
China's Council for International Cooperation on Environment and Development
![]() Dr. DeLaquil was the lead MARKAL analyst working with Princeton and Tsinghua University to determine the impact of advanced technologies to meet China’s future energy demand, improve urban air quality, limit oil and gas imports and reduce GHG emissions. The results of the studies, which were briefed to the Vice Premier in 2003, indicated an early need to develop renewable energy and energy efficiency, and a longer term need to transition away from coal combustion and towards coal gasification for both electricity generation and liquid fuels production.
Dr. DeLaquil was the lead MARKAL analyst working with Princeton and Tsinghua University to determine the impact of advanced technologies to meet China’s future energy demand, improve urban air quality, limit oil and gas imports and reduce GHG emissions. The results of the studies, which were briefed to the Vice Premier in 2003, indicated an early need to develop renewable energy and energy efficiency, and a longer term need to transition away from coal combustion and towards coal gasification for both electricity generation and liquid fuels production.
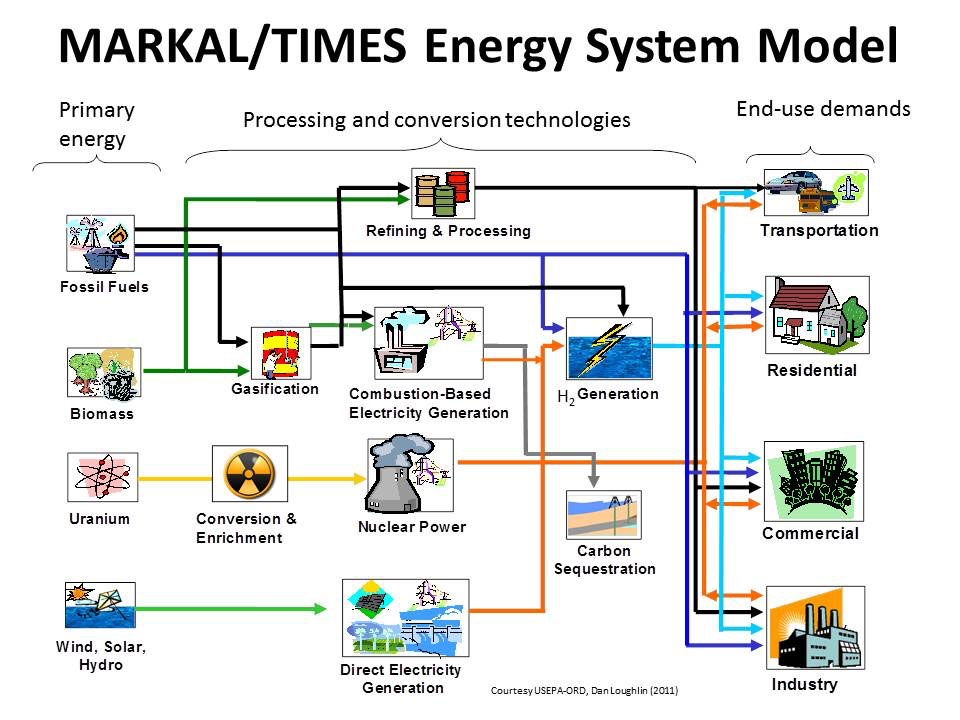
TIMES Documentation
Loulou, R., Remme, U., Kanudia, A., Lehtila, A., Goldstein, G., Documentation for the TIMES Model, International Energy Agency - Energy Technology Systems Analysis Programme, 2005
https://iea-etsap.org/index.php/documentation
MARKAL Documentation
Loulou, R., Goldstein, G., Noble, K., “Documentation for the MARKAL Family of Models,” International Energy Agency – Energy Technology System Analysis Programme, October 2004 (http://www.etsap.org/documentation.asp)
International Energy Agency – Energy Technology Systems Analysis Program (IEA-ETSAP)
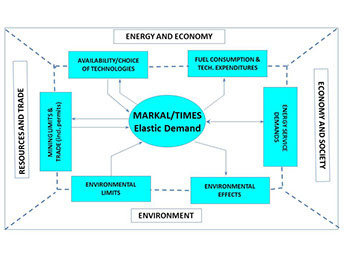 IEA-ETSAP is the longest running Implementing Agreement of the IEA, begun in 1976. The ETSAP Contracting Parties (currently 18) embark on common programs of work looking to advance the state of the art of integrated energy system model through its development, stewardship and application of the MARKAL/TIMES family of models. The platform has been embraced by nearly 300 institutions in about 70 countries to examine energy policy and strategic planning issues, including climate change mitigation. In addition, multi-region models have been assembled covering Europe, the US, ASEAN countries, Southeast Europe and Eurasia, Canada, and the Nordic counties. The global TIMES Integrated Assessment Model (TIAM) includes a simple climate module to enable long-run GHG concentration to be factored into the analysis. An extensive list of studies undertaken by the IEA-ETSAP partners and collaborating institution using MARKAL/TIMES can be found on the website.
IEA-ETSAP is the longest running Implementing Agreement of the IEA, begun in 1976. The ETSAP Contracting Parties (currently 18) embark on common programs of work looking to advance the state of the art of integrated energy system model through its development, stewardship and application of the MARKAL/TIMES family of models. The platform has been embraced by nearly 300 institutions in about 70 countries to examine energy policy and strategic planning issues, including climate change mitigation. In addition, multi-region models have been assembled covering Europe, the US, ASEAN countries, Southeast Europe and Eurasia, Canada, and the Nordic counties. The global TIMES Integrated Assessment Model (TIAM) includes a simple climate module to enable long-run GHG concentration to be factored into the analysis. An extensive list of studies undertaken by the IEA-ETSAP partners and collaborating institution using MARKAL/TIMES can be found on the website.
IEA-ETSAP provides training and support for the global MARKAL/TIMES modeling community. Evaluation version of MARKAL/TIMES with the supporting model management systems (VEDA and ANSWER) may be obtained by completing the User Registration form and executing the ETSAP Letter of Agreement governing access to the model generators source code.
Since its inception Mr. Goldstein has been involved in IEA-ETSAP, while at Brookhaven National Laboratory he was responsible for documenting, maintaining and supporting the initial (mainframe-based) incarnation of MARKAL, and later migrating MARKAL, implementing MACRO, and developing the first model management system (MARKAL Users’ Support System) on personal computers. Since 1992 he has been directly engaged by IEA-ETSAP as first the Primary Systems Coordinator (during the phase of IEA-ETSAP when the most active model and management development was being undertaken) and now as the Liaison Officer (as collaboration and outreach become increasingly a focus of IEA-ETSAP)
IEA-ETSAP TIMES-Starter Platform
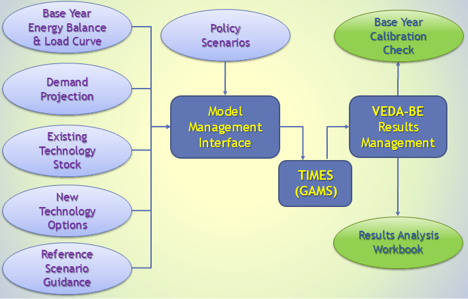 With support from the IEA-ETSAP consortium, DWG developed the TIMES-Starter platform as a new approach to building a TIMES energy system optimization model. Although TIMES is the most widely used least-cost optimization methodology employed to inform energy (and water) policy and strategic planning, the time and cost of developing a model from scratch is a significant barrier to many developing countries. The TIMES-Starter platform provides an integrated full-sector energy system model (that may include non-energy sectors and water if desired) that employs best practices and is built upon a peer-reviewed database. The model is assembled in a set of interactive Excel templates that are readily customized to a base-year energy balance, resource supply and power generation mix. It has a comprehensive model management platform that overseas all aspects of working with TIMES including integration of the Excel workbooks, RES diagramming, various technology views, job submission, along with dynamic pivot tables and an interactive multi-case graphical comparison and metrics workbook to facilitate interpreting model results and their communication to decision-makers. DWG has introduced the Starter platform in Turkey, China (on behalf of the IEA) and Costa Rica. Given the success of the ANSWER-based TIMES-Starter platform IEA-ETSAP has engaged DWG to develop a 2nd generation TIMES-Starter under the VEDA Front-End (VEDA-FE) system.
With support from the IEA-ETSAP consortium, DWG developed the TIMES-Starter platform as a new approach to building a TIMES energy system optimization model. Although TIMES is the most widely used least-cost optimization methodology employed to inform energy (and water) policy and strategic planning, the time and cost of developing a model from scratch is a significant barrier to many developing countries. The TIMES-Starter platform provides an integrated full-sector energy system model (that may include non-energy sectors and water if desired) that employs best practices and is built upon a peer-reviewed database. The model is assembled in a set of interactive Excel templates that are readily customized to a base-year energy balance, resource supply and power generation mix. It has a comprehensive model management platform that overseas all aspects of working with TIMES including integration of the Excel workbooks, RES diagramming, various technology views, job submission, along with dynamic pivot tables and an interactive multi-case graphical comparison and metrics workbook to facilitate interpreting model results and their communication to decision-makers. DWG has introduced the Starter platform in Turkey, China (on behalf of the IEA) and Costa Rica. Given the success of the ANSWER-based TIMES-Starter platform IEA-ETSAP has engaged DWG to develop a 2nd generation TIMES-Starter under the VEDA Front-End (VEDA-FE) system.
TIMES-Starter Model Guidelines
DWG Analytics Workbook
![]() The DWG Analytics workbook is a DWG proprietary tool that can contain the results from dozens of MARKAL/TIMES model scenarios and organizes the results in a large number of standard multi-case comparison graphs. The workbook is automatically updated from the VEDA-BE results handling tool whenever new scenario results are generated. An important feature of the Analytics workbook is that the user can select the scenarios for comparisons, typically looking at 3 or 4 scenarios at a time. The Analytics workbook serves as the primary tool for understanding the model results. There are comparison graphics, showing both the actual values and the difference from the first scenario in the comparison set. Additional metrics are available, which show base year and milestone year shares and differences, as well as growth and cumulative change.
The DWG Analytics workbook is a DWG proprietary tool that can contain the results from dozens of MARKAL/TIMES model scenarios and organizes the results in a large number of standard multi-case comparison graphs. The workbook is automatically updated from the VEDA-BE results handling tool whenever new scenario results are generated. An important feature of the Analytics workbook is that the user can select the scenarios for comparisons, typically looking at 3 or 4 scenarios at a time. The Analytics workbook serves as the primary tool for understanding the model results. There are comparison graphics, showing both the actual values and the difference from the first scenario in the comparison set. Additional metrics are available, which show base year and milestone year shares and differences, as well as growth and cumulative change.
Collaboration with Software Developers
GAMS Development Corporation (www.gams.com)
GAMS is a modeling language evolving out of the World Bank in the mid-1980s that has become the stalwart platform for the development of advanced optimization models, and has been the acknowledged leader in the field for over 20 years.
Working with Professor Alan Manne of Stanford University in the early 1990s, Mr. Goldstein moved the MARKAL model generator off mainframe computers and from its original BNL OMNI modeling platform to GAMS. MARKAL and now TIMES are both written in the GAMS modeling language. Mr. Goldstein coordinates with ETSAP and the model management “shell” developers (below) to ensure that GAMS works seamlessly with their systems to realize a smooth operating environment for MARKAL/TIMES users. He works closely with GAMS to advance the modeling platform, and provides world-wide support for MARKAL/TIMES users with respect to GAMS on their behalf.
KanORS Energy Modeling and Research (KanORS-EMR, http://www.kanors-emr.org/)
Headed by Dr. Amit Kanudia, KanORS is a leader in the advanced application of MARKAL/TIMES and the developer of the VErsatile Data Analysis (VEDA) model management system and web-based VEDA-Visualization system. The cutting edge models developed and applied by KanORS include the TIMES Integrated Assessment Model (TIAM), pan-European TIMES model (PET), and several detailed country models including for Japan and most recently India and others. Also, in collaboration with DWG KanORS has spearheaded the development of the highly regionalized US FACETS model, and the EC-TIMES pan Energy Community planning model. KanORS also plays an ongoing contributing role for the IEA-ETSAP consortium.
Noblesoft Systems (www.noblesoft.com.au)
Headed by Dr. Ken Noble, Noblesoft developed and supports the ANSWER model management system for MARKAL and TIMES. ANSWER, the 1st Windows base interface for MARKAL, was developed by Dr. Noble while at ABARE, has over 100 users world-wide. Noblesoft also plays an ongoing contributing role for the IEA-ETSAP consortium.
Regional Economic Modeling Inc. (REMI) MARKAL to REMI Interface (www.remi.com)
DWG and REMI have conducted joint research to develop the methodology for bi-directional linking of MARKAL/TIMES and REMI models. The REMI-2-MARKAL link provides useful energy demand projections to MARKAL and MARKAL feeds investment, expenditure and fuel price/consumption indicators to REMI. The theoretical foundation was established, an initial partial implementation has been carried out and the linkage process is ready for application.
Training and Capacity Building
 DWG is an acknowledged leader in multi-country and multi-institution capacity building, as noted in the RESMD and Pak-IEM projects. Mr. Goldstein, serving as the IEA-ETSAP Primary Systems Coordinator and Liaison Officer has provided training to hundreds of individuals from around the world. He provided in-depth training to experts at US Department of Energy, US Environmental Protection Agency, US national laboratories, and others. He has also been asked to conduct introductory as well as specialized and advanced MARKAL/TIMES modeling courses by numerous government, research and university institutions from Albania, Armenia, Austria, Australia, Belgium, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Brazil, Bulgaria, Canada, China, Colombia, Croatia, Germany, Georgia, Hong Kong, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Kosovo, Kuwait, Latvia, Macedonia, Moldova, Netherlands, Norway, Pakistan, Puerto Rico, Romania, Serbia, Singapore, South Africa, South Korea, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, Ukraine, United Kingdom, and the United States.
DWG is an acknowledged leader in multi-country and multi-institution capacity building, as noted in the RESMD and Pak-IEM projects. Mr. Goldstein, serving as the IEA-ETSAP Primary Systems Coordinator and Liaison Officer has provided training to hundreds of individuals from around the world. He provided in-depth training to experts at US Department of Energy, US Environmental Protection Agency, US national laboratories, and others. He has also been asked to conduct introductory as well as specialized and advanced MARKAL/TIMES modeling courses by numerous government, research and university institutions from Albania, Armenia, Austria, Australia, Belgium, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Brazil, Bulgaria, Canada, China, Colombia, Croatia, Germany, Georgia, Hong Kong, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Kosovo, Kuwait, Latvia, Macedonia, Moldova, Netherlands, Norway, Pakistan, Puerto Rico, Romania, Serbia, Singapore, South Africa, South Korea, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, Ukraine, United Kingdom, and the United States.